Abstract
Introduction Treatment of patients with high grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements (HGBL-DH/TH) with intensified immune-chemotherapy DA-EPOCH-R results in a 48-month event-free survival of 71.0% [Dunleavy, Lancet Haematol 2018]. In the HOVON-152, we investigate the added value of immune checkpoint PD-1 inhibition for patients who achieve complete metabolic remission (CMR) after DA-EPOCH-R induction. Nonetheless, whether DA-EPOCH-R has an effect on the immune system, and - reversely - whether the composition of immune system influences DA-EPOCH-R therapy are not known. To gain more insight on these important issues, we performed longitudinal high-throughput immune profiling of patients during the DA-EPOCH-R induction phase of the HOVON-152.
Methods In the HOVON-152 single arm, phase II trial (NCT03620578) HGBL-DH/TH patients received 1 cycle of R-CHOP followed by 5 cycles of DA-EPOCH-R induction treatment. Peripheral blood was sampled after one cycle of R-CHOP (enrollment), before start of the 3rd DA-EPOCH-R cycle (midterm) and after the last DA-EPOCH-R cycle (end-of-induction, EOI). Patients achieving CMR at EOI (Deauville score 1-3 after induction) were identified as responders and proceeded with nivolumab consolidation (480 mg iv every 4 weeks) for 1 year.
For the profiling we selected 55 patients (32 responders and 23 non-responders, enriched for non-responders) who completed the whole study. T and NK cells were enumerated through quantitative, dual platform flow cytometry of unseparated full blood. The frequencies of NK and T cell subsets were determined in cryopreserved PBMC through multiparameter flow cytometry. The high-throughput flow cytometry data were analyzed by computational methods UMAP and FlowSOM. Non-parametric methods were used for statistical testing.
Results DA-EPOCH-R had no apparent effects on the total number of NK cells. The frequency of cytotoxic CD56dim NK cells was, however, gradually decreased during DA-EPOCH-R (p<0.001), consistent with rituximab-mediated consumption. There was also a gradual decrease in NK cells expressing maturation markers CD57 (p=0.001), TIGIT (p=0.009) and KLRG1 (p=0.027) and a transient decrease in DNAM1 (p<0.001). Consistently, the proportion of CD56bright CD16dim non-cytotoxic NK cells and the frequency of NK cells expressing inhibitory receptor NKG2A became more abundant (all p<0.001). Despite losing the cytotoxic CD56dimphenotype, the NK cells showed activation induced alterations such as the progressive increase of NKp30 (p<0.001) and transient increase of HLA-DR (p<0.001) during therapy.
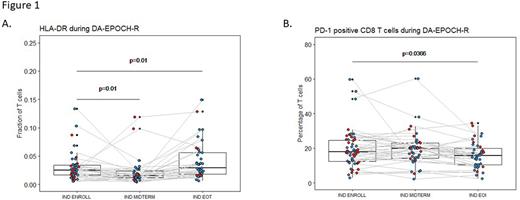
More interestingly, DA-EPOCH-R appeared to have significant impact on T cells: while total T cell frequencies and numbers showed only a temporary decrease at midterm, a progressive decrease in the CD4/CD8 ratio (p=0.016) and a progressive increase in the expression of T cell activation markers CD127 (p<0.01) and CD38 (p=0.004) was clearly visible. HLA-DR, another activation marker, also showed an increase at EOI (p=0.01) after a transient decrease at midterm (p=0.01) (Figure 1A). The analysis of exhaustion markers TIM3, LAG3 and TIGIT revealed a transient increase of LAG3 on CD8 cells (p≤0.018). Most remarkably, DA-EPOCH-R treatment was significantly associated with a progressive decline in the frequency of PD-1 positive CD8 T cells (p=0.037) (Figure 1B). Also interestingly, the responding patients tended to have lower PD-1 levels on their T cells at the end of treatment as compared to non-responders (p=0.052).
Further analyses regarding the possible impact of immune system on DA-EPOCH-R outcome revealed that a (relative) abundance of non-cytotoxic CD56bright NK cells (p=0.006) and higher CD3 T cells (p=0.04) at enrollment was associated with achievement of CMR.
Conclusion In conclusion, treatment of HGBL-DH/TH patients with DA-EPOCH-R results not only in the expected rituximab-mediated alterations in the NK cell compartment, but also influences the T cell compartment with a shift towards a lower CD4/CD8 ratio, more T cell activation and a reduction of PD-1 expression on CD8 T cells. Higher T cell frequencies at baseline and decreased frequencies of PD-1+ CD8 T cells at EOI were furthermore associated with achievement of CMR. Overall, these data contribute to a wider understanding of NK and T cell dynamics during DA-EPOCH-R and points to an considerable involvement of T cells in therapy outcome.
Disclosures
Nijland:Takeda: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Genmab: Consultancy. Klerk:Roche: Other: speaker fee (ASH). Mutseaers:Glaxo Smith Kline: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy. Mutis:Janssen: Research Funding; Genmab: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Chamuleau:Genmab: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Gilead: Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Nivolumab as immune checkpoint inhibitor (inhibiting PD-1) in consolidation phase for the treatment of DH/TH-HGBL patients
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.